Otterhound
Also known as: None
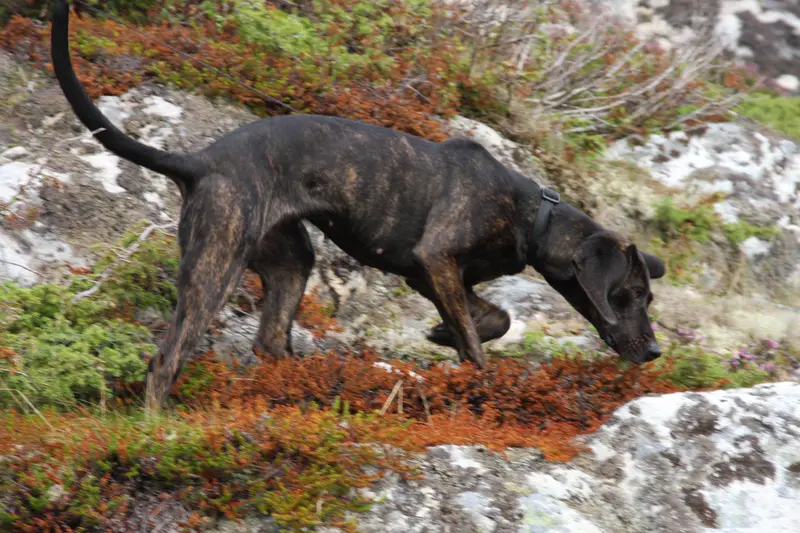
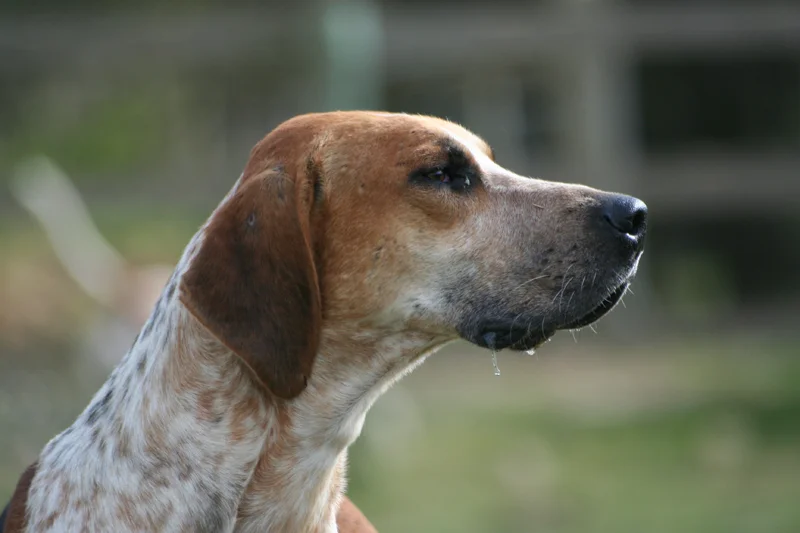
The Otterhound is a large, affectionate breed known for its unique swimming abilities and friendly nature. Originally bred for hunting otters, they thrive in active families and require regular exercise.
⚡At a glance
🏆Best traits
Key Facts
- Height
- 60.96-68.58 cm
- Weight
- 36.29-52.16 kg
- Life Span
- 10 - 13 years
- Group
- Hound
- Origin
- England
- Shedding
- Low
- Exercise
- 90 min/day
- Best For
- Families
Overview
🐕Breed Overview
✨Key Traits
💡What Makes Otterhound Special
The Otterhound's most defining traits include its strong swimming ability, friendly disposition, and unique vocalizations. They are natural trackers with an exceptional sense of smell, making them excellent companions for outdoor enthusiasts.
Their webbed feet and water-resistant coat allow them to excel in aquatic environments, and they often enjoy swimming and playing in water. Despite their hunting background, Otterhounds are gentle and affectionate, making them suitable family pets.
Their stubbornness can pose challenges during training, but with patience and positive reinforcement, they can learn basic commands and manners. Overall, Otterhounds are loyal companions that thrive in active households where they can engage in various activities with their families.
The Otterhound is a large, affectionate breed with a rich history as a hunting companion. Originally bred in England for otter hunting, this unique breed possesses webbed feet and a water-resistant coat, making it an excellent swimmer. Otterhounds are known for their amiable and boisterous personalities, often forming strong bonds with their families.
They thrive in active households where they can enjoy outdoor adventures, especially swimming and exploring nature. Despite their hunting background, Otterhounds are gentle and good with children, making them suitable family pets. However, their stubbornness can pose challenges during training, requiring patience and consistency from owners.
With proper exercise and socialization, Otterhounds can adapt to various living situations, though they do best in homes with ample outdoor space. As one of the most endangered native breeds in Britain, the Otterhound is a rare gem that brings joy and companionship to those who appreciate its unique qualities.
🎉Fun Facts
Otterhounds are one of the rarest dog breeds in the world, with an estimated population of only 1000.
Otterhounds have a unique double coat that is both water-resistant and rough to the touch.
Otterhounds have webbed feet, making them excellent swimmers.
They are known for their deep, melodious bay that can be heard from a distance.
They were historically used to hunt otters, which were considered pests to fish populations.
Breed Characteristics
Family & Friends
Good Behavior
Get Up & Go
Household Harmony
Temperament & Personality
🐕Core Temperament
The Otterhound is characterized by its amiable and boisterous temperament. They are friendly and affectionate with their families, often forming strong bonds with children and other pets.
While they are generally easygoing, they can be stubborn and may not always respond to commands, particularly when they are outdoors and distracted by scents. Their inquisitive nature drives them to explore their surroundings, which can lead to wandering if not properly supervised.
Despite their hunting background, Otterhounds are not aggressive and are known for their gentle demeanor. They thrive on companionship and enjoy being part of family activities, making them excellent family pets.
💫Personality Profile
Otterhounds are known for their friendly and boisterous nature. They are affectionate with their families and generally get along well with children and other pets.
Their playful demeanor makes them a joy to have around, although they can be a bit rough during play. While they are sociable and enjoy companionship, they can also exhibit stubbornness, particularly when distracted by scents outdoors.
This breed thrives on human interaction and can become bored or anxious if left alone for long periods. Their inquisitive nature means they require supervision when outdoors, as they may wander off in pursuit of interesting smells.
🔊Vocal Tendencies
Otterhounds are known for their distinctive, deep baying voice, which they use frequently. They may bark to alert their owners of visitors or when they are excited.
Their vocalizations can carry over long distances, making them effective watchdogs. However, their friendly nature means they are not typically aggressive barkers.
They may also whine or make other sounds when seeking attention or expressing their needs.
Affection & Social Traits
Big-hearted and highly social — here’s how it shows up day to day.
Energy & Activity
Calmer, low-energy vibe — great for matching your routine.
Communication Style
Expressive and vocal — a quick read on noise at home.
Care Requirements
🏃♂️Exercise Requirements
Daily Exercise
Otterhounds require a good amount of daily exercise to maintain their physical and mental health. Ideally, they should engage in at least 60 to 90 minutes of exercise each day, which can be broken down into multiple sessions.
Activities such as long walks, swimming, and playtime in a secure area are excellent for this breed, as they enjoy being in the water due to their webbed feet. Puppies may require shorter, more frequent play sessions to accommodate their developing bodies, while senior otterhounds may benefit from gentler, low-impact activities to avoid strain on their joints.
Regular exercise helps prevent obesity, supports cardiovascular health, and reduces behavioral issues that can arise from boredom or pent-up energy. Insufficient exercise can lead to weight gain, destructive behavior, and increased anxiety.
Preferred Activities
🏠Living & Adaptability
Space Requirements
Otterhounds thrive in environments where they have ample space to roam and explore. Ideally, they should have access to a large, securely fenced yard where they can run and play freely.
While they can adapt to apartment living if given sufficient exercise, they are best suited for homes with outdoor space due to their size and energy levels. Owners in smaller living situations should ensure they can provide daily walks and mental stimulation to keep their otterhound happy.
The breed's tendency to jump high means that fences should be at least 5 feet tall to prevent escapes. Without adequate space and supervision, otterhounds may exhibit destructive behaviors or anxiety.
Climate Preference
🍲Feeding Guide
Schedule
Food Types
Portion Size
Special Nutritional Needs
Otterhounds may benefit from a diet rich in omega fatty acids to support their skin and coat health, particularly due to their oily undercoat. It's essential to monitor their weight, as they can be prone to obesity if overfed. Regular veterinary check-ups can help identify any specific dietary needs or sensitivities.
✨Grooming Requirements
Grooming Overview
The Otterhound's coat requires regular grooming to keep it healthy and free from mats. Weekly brushing is essential to remove loose hair and debris, particularly from their long, shaggy beard and webbed feet, which can trap dirt and moisture.
Bathing should be done as needed, typically every few months, to avoid stripping the coat of its natural oils. Owners should also clean their Otterhound's ears weekly to prevent infections, given their long, droopy ears.
Regular nail trimming is necessary to keep their feet healthy and comfortable.
Care Schedule
Brush weekly, bathe as needed (approximately every 2-3 months), and trim nails every 2-4 weeks.
Health Profile
⚕️Health Care
Regular health care is crucial for the Otterhound's longevity. Routine veterinary check-ups, vaccinations, and preventive treatments can help detect and address health issues early.
Maintaining a balanced diet, providing regular exercise, and monitoring for any changes in behavior or health can significantly impact their overall well-being. Owners should also be proactive in managing any breed-specific health concerns, such as hip dysplasia or ear infections, through appropriate care and lifestyle adjustments.
Health Issues Overview
⏳Average Lifespan
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in the Otterhound's lifespan, with hereditary health issues such as hip dysplasia and epilepsy being common concerns. Responsible breeding practices that prioritize genetic diversity can help mitigate these risks.
Potential owners should seek out reputable breeders who conduct health testing and provide transparency about the lineage of their puppies. Understanding the genetic background of the breed can aid in making informed decisions about health management and care.
Living Conditions
The Otterhound's lifespan can be influenced by various environmental factors, including housing conditions, exercise routines, and social interactions. Dogs living in secure, spacious environments with regular outdoor activities tend to live longer, healthier lives.
Access to water for swimming is particularly beneficial for this breed, as it aligns with their natural instincts. Additionally, social interactions with humans and other dogs can positively impact their mental well-being, reducing stress and anxiety, which can contribute to a longer lifespan.
🏥Common Health Issues
Epilepsy
Warning Signs
🔬Diagnosis
Neurological examination and ruling out other causes.
💊Treatment
Anticonvulsant medications.
📝Management Tips
Regular veterinary check-ups and medication as prescribed.
Hip Dysplasia
Warning Signs
🔬Diagnosis
X-rays and physical examinations by a veterinarian.
💊Treatment
Pain management, weight control, and in severe cases, surgical intervention.
📝Management Tips
Maintain a healthy weight, avoid excessive jumping during growth, and provide joint supplements if recommended by a vet.
Elbow Dysplasia
Warning Signs
🔬Diagnosis
Veterinary examination and imaging techniques.
💊Treatment
Pain management and possible surgical options.
📝Management Tips
Similar to hip dysplasia, maintain a healthy weight and limit high-impact activities during growth.
Ear Infections
Warning Signs
🔬Diagnosis
Veterinary examination of the ear canal.
💊Treatment
Antibiotic or antifungal ear drops as prescribed.
📝Management Tips
Regular ear cleaning and monitoring for signs of infection.
Bloat (Gastric Torsion)
Warning Signs
🔬Diagnosis
Physical examination and imaging.
💊Treatment
Emergency veterinary intervention is required.
📝Management Tips
Feed smaller meals, avoid vigorous exercise after eating, and monitor for signs of distress.
🛡️Preventive Care
🔬Hip Evaluation
Hip Evaluation assesses the hip joints for dysplasia and other abnormalities, which can affect mobility and quality of life.
📅 Recommended at 12 months and again at 2 years, then every 2-3 years thereafter.
🔬Elbow Evaluation
Elbow Evaluation checks for dysplasia and other elbow joint issues that can lead to lameness.
📅 Recommended at 12 months and again at 2 years, then every 2-3 years thereafter.
🔬DNA for Thrombopathy
DNA testing for thrombopathy identifies potential bleeding disorders that can affect the breed.
📅 Recommended for breeding dogs and those with a family history of bleeding issues.
Training
🧠Intelligence & Trainability
💪Work Drive
Otterhounds have a strong work drive rooted in their history as hunting dogs. They thrive on tasks that engage their senses, particularly scent work.
Activities such as tracking, scent detection, and even participating in dog sports can provide the mental stimulation they need. Regular engagement in these activities is essential to keep them happy and prevent boredom.
Without sufficient mental and physical challenges, they may resort to undesirable behaviors, such as digging or excessive barking.
⚠️Training Considerations
Otterhounds can be somewhat stubborn and may not always respond to commands, especially when they detect an interesting scent outdoors. This can make training a challenge, as they may become easily distracted.
To overcome these challenges, consistent and positive reinforcement training methods are recommended. Engaging them in scent work or tracking activities can also help channel their natural instincts into productive training sessions.
Early socialization is crucial to help them become well-adjusted adults, and owners should be patient and persistent in their training efforts, using treats and praise to motivate their Otterhound.
📝Training Tips
Training an Otterhound requires patience and creativity. Start with basic obedience commands and gradually introduce more complex tasks. Use positive reinforcement techniques, such as treats and praise, to encourage desired behaviors.
Incorporating fun activities like scent games can keep their interest and make training enjoyable. Consistency is key; establish a routine and stick to it. Socialization with other dogs and people from a young age is essential to help them develop good manners and reduce any potential stubbornness.
Owners should be prepared for a longer training process, as Otterhounds may take time to fully grasp commands.
History & Heritage
📜Origin Story
The Otterhound is believed to have originated in France, with its early ancestors resembling the old French Vendeen hound. The breed was brought to England, where it became integral to otter hunting, particularly in the northwest regions.
King John is noted to have kept the first documented packs of Otterhounds in the early 13th century. The breed's popularity peaked in the late 19th century, but with the decline of otter populations and the subsequent ban on hunting, the Otterhound faced a significant reduction in numbers.
Today, it is considered one of the most endangered native breeds in Britain, with ongoing efforts to maintain its lineage and promote its qualities as a companion dog.
⏳Development History
The Otterhound's development can be traced back to the early 19th century in England, with influences from French hounds such as the Griffon Vendeen. The breed was specifically developed for hunting otters, utilizing its keen sense of smell and strong swimming abilities.
Over time, the breed has seen a decline in numbers due to the ban on otter hunting, leading to its current status as a vulnerable breed. Despite this, dedicated breeders and enthusiasts continue to work towards preserving the Otterhound's unique traits and characteristics.
🛡️Purpose & Historical Role
Originally bred for hunting otters, the Otterhound played a crucial role in controlling otter populations that threatened fish stocks in rivers and streams. The breed's strong sense of smell and swimming ability made it an effective hunter, trailing otters to their dens and alerting hunters. Although otter hunting has ceased, the Otterhound has transitioned into a companion role, valued for its friendly nature and loyalty.
🏺Cultural Significance
The Otterhound has a rich history tied to the sport of otter hunting in England, dating back to the medieval period. Although otter hunting has been banned since 1978, the breed's legacy continues as a companion animal.
The Otterhound is recognized as a vulnerable native breed in the UK, with efforts underway to preserve its lineage. Its unique characteristics, such as webbed feet and a water-resistant coat, highlight its adaptability to aquatic environments, making it a beloved breed among outdoor enthusiasts.
The breed has also made appearances in literature and art, further solidifying its place in British culture.
Conservation Status
Population is considered vulnerable or declining in many regions.
Hard to find outside select breeders or regions of origin.
This breed is endangered with low population numbers globally.
?Frequently Asked Questions
Is the Otterhound good for apartment living?
The Otterhound may struggle with apartment living. They typically need more space and a yard to expend their energy. If you live in an apartment, you would need to commit to extensive daily exercise and outdoor time to keep this breed happy.
How much does a Otterhound shed?
The Otterhound sheds minimally compared to many other breeds. While no dog is truly hypoallergenic, this breed produces less loose hair than average. Routine brushing will help manage the little shedding they do.
Are Otterhounds easy to train?
The Otterhound may struggle with training and requires extra patience and consistency. They tend to be independent thinkers who may not always follow commands readily. Positive reinforcement and short, engaging training sessions work best.
How long do Otterhounds live?
The average lifespan of a Otterhound is 10 - 13 years. Lifespan can be influenced by genetics, diet, exercise, and overall health care. Regular veterinary check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can help your Otterhound live a long and happy life.
Is the Otterhound good with kids?
Yes, the Otterhound generally does well with children. They are patient and affectionate, making them a solid family dog. As with any breed, supervision during interactions with young children is always recommended.
How much exercise does a Otterhound need?
The Otterhound requires approximately 90 minutes of daily exercise. A combination of walks, play sessions, and mental stimulation activities will help keep them fit and happy. This is a moderate exercise requirement that fits well into most active lifestyles.
Is the Otterhound good with other pets?
Yes, the Otterhound generally does well with other pets. Their friendly and adaptable nature helps them coexist peacefully in multi-pet households. Early socialization helps ensure the best relationships with other animals.