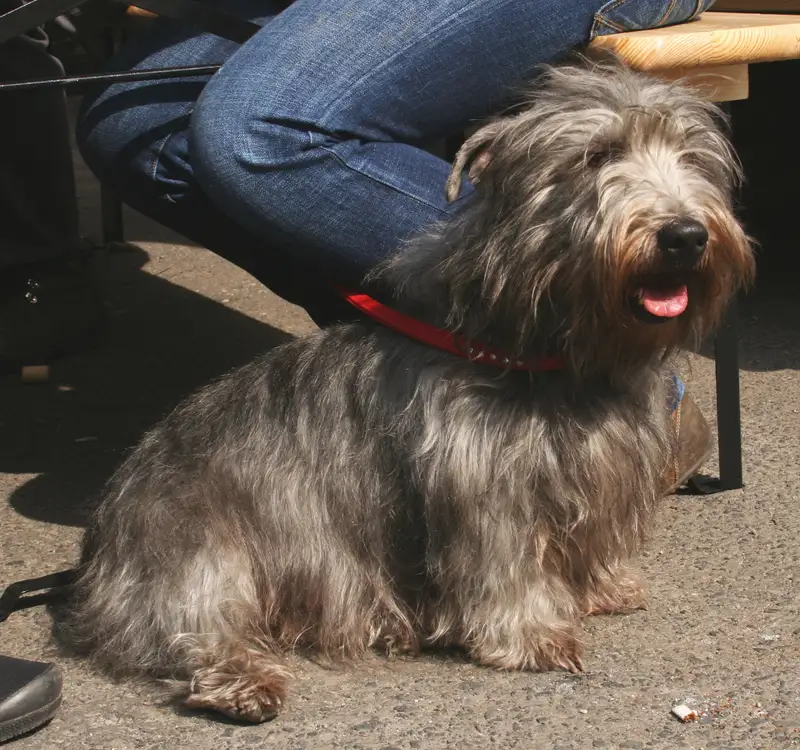
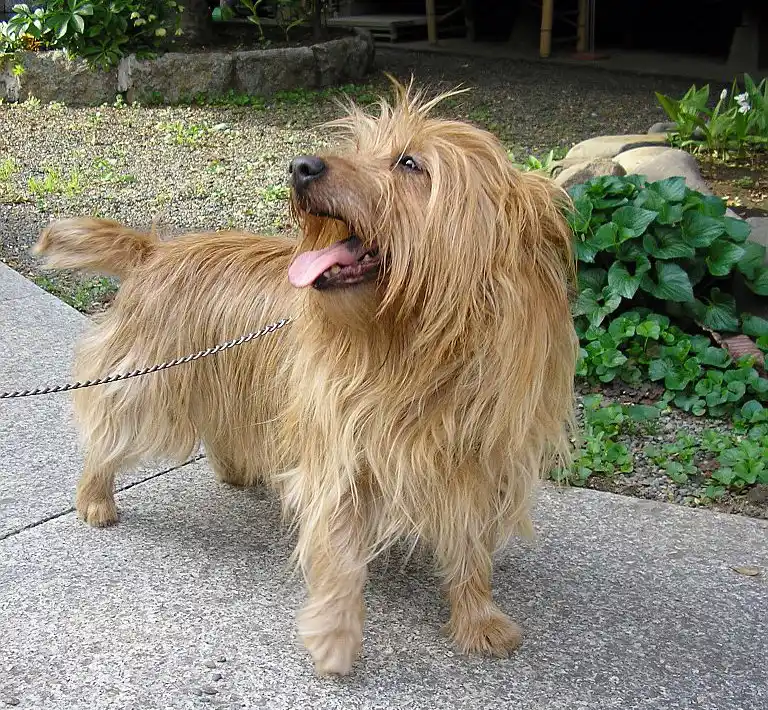
Miniature Schnauzer
Also known as: Mini Schnauzer, Zwergschnauzer
The Miniature Schnauzer is a small, spirited dog known for its playful personality and alert nature. Originally bred for vermin control, they are now cherished as affectionate companions and effective watchdogs. With a wiry coat and distinctive facial furnishings, they thrive on human companionship and require regular exercise and mental stimulation.
⚡At a glance
🏆Best traits
Key Facts
- Height
- 30-36 cm
- Weight
- 4.5-8.2 kg
- Life Span
- 12 - 14 years
- Group
- Terrier
- Origin
- Germany
- Shedding
- Very Low
- Exercise
- 30 min/day
- Best For
- Apartments, Families
Overview
🐕Breed Overview
✨Key Traits
💡What Makes Miniature Schnauzer Special
The Miniature Schnauzer's key traits include its alertness and intelligence, making it an excellent watchdog. They are playful and enjoy interactive play, which helps to keep them mentally stimulated.
Their affectionate nature allows them to bond closely with their families, and they often seek companionship. Despite their small size, they possess a strong personality and can be quite spirited.
Their adaptability to various living situations, including apartments, makes them suitable for many families. However, their high prey drive means they may not be the best fit for homes with small pets unless properly socialized.
The Miniature Schnauzer is a charming small dog that has captured the hearts of many with its spirited personality and distinctive appearance. Originating in Germany in the late 19th century, this breed was developed from the Standard Schnauzer, Affenpinscher, and possibly the Poodle, primarily for the purpose of vermin control on farms. Today, they are cherished as affectionate companions and effective watchdogs.
With a height of 12 to 14 inches and a weight ranging from 10 to 18 pounds, Miniature Schnauzers are compact yet sturdy, boasting a wiry double coat that comes in three recognized colors: salt and pepper, black and silver, and solid black. Their unique facial furnishings, including a bushy beard and eyebrows, add to their endearing charm. Known for their alertness and intelligence, Miniature Schnauzers are often described as "spunky" and playful, making them excellent family pets.
They are friendly and eager to please, but they can also be somewhat aloof with strangers, making them effective watchdogs. Their high energy levels require regular exercise, including daily walks and playtime, to keep them mentally and physically stimulated. Without sufficient activity, they may become bored and engage in undesirable behaviors.
Training a Miniature Schnauzer can be a rewarding experience, as they are generally easy to train due to their intelligence and willingness to learn. However, their stubborn streak may require patience and consistency from their owners. Early socialization and positive reinforcement techniques are essential to ensure they develop into well-rounded companions.
In terms of health, Miniature Schnauzers are generally robust, with a lifespan of 12 to 14 years. However, they can be prone to certain health issues, including hyperlipidemia, diabetes, and eye problems. Regular veterinary check-ups and a balanced diet are crucial for maintaining their health.
Overall, the Miniature Schnauzer is a delightful breed that thrives on human companionship and enjoys being part of family activities. Their playful nature, intelligence, and adaptability make them a perfect fit for various lifestyles, from active families to individuals seeking a loyal companion.
🎉Fun Facts
Miniature Schnauzers are known for their distinctive beards and eyebrows, which require regular grooming to maintain their appearance.
Miniature Schnauzers can excel in various dog sports, including agility and obedience competitions.
The breed has a strong history as a watchdog, often barking to alert their owners of any intruders.
They are one of the few terrier breeds not derived from British origins, having been developed in Germany.
Breed Characteristics
Family & Friends
Good Behavior
Get Up & Go
Household Harmony
Temperament & Personality
✨Key Traits
🐕Core Temperament
The Miniature Schnauzer is characterized by its alert and spirited temperament. They are friendly, intelligent, and eager to please, making them excellent companions.
While they are generally not aggressive, they can be protective of their families and may bark at strangers. Their playful nature and high energy levels require regular exercise and mental stimulation to keep them happy.
With proper training and socialization, they can thrive in family environments and get along well with children and other pets.
💫Personality Profile
Miniature Schnauzers are known for their lively and spirited nature. They are affectionate with their families and enjoy being involved in daily activities.
While they can be somewhat aloof with strangers, they warm up quickly once introduced. Their playful demeanor makes them great companions for children, and they thrive on interaction and engagement.
However, they can be vocal, often barking to alert their owners of any perceived threats. This breed is intelligent and eager to please, making them relatively easy to train, though their stubborn streak may require patience from their owners.
🔊Vocal Tendencies
Miniature Schnauzers are known for their vocal tendencies, often barking to alert their owners of any intruders or unusual sounds. They may bark when excited, during play, or when greeting visitors.
While they are not excessively noisy, their alert nature means they will vocalize when they feel it is necessary. Proper training and socialization can help manage their barking tendencies, ensuring they are well-mannered in various situations.
Affection & Social Traits
Warm and balanced socially — here’s how it shows up day to day.
Energy & Activity
Moderate, steady energy — great for matching your routine.
Communication Style
Expressive and vocal — a quick read on noise at home.
Care Requirements
🏃♂️Exercise Requirements
Daily Exercise
Miniature Schnauzers require regular exercise to maintain their physical and mental health. Ideally, they should engage in at least 30 to 60 minutes of exercise daily, which can be broken down into two or three sessions.
Activities such as brisk walks, playtime in the yard, or engaging in dog sports like agility or obedience training are excellent for this breed. Puppies may require shorter, more frequent play sessions, while senior dogs may benefit from gentler activities to accommodate their energy levels.
Regular exercise helps prevent boredom, which can lead to destructive behaviors, and supports weight management, cardiovascular health, and overall happiness. Without sufficient exercise, Miniature Schnauzers may become hyperactive or develop behavioral issues.
Preferred Activities
🏠Living & Adaptability
Space Requirements
Miniature Schnauzers are adaptable and can thrive in various living environments, including apartments, as long as they receive adequate exercise and mental stimulation. A small yard is ideal, but regular walks and playtime can compensate for limited outdoor space.
Owners in smaller living situations should ensure their dogs have opportunities for physical activity and mental engagement to prevent boredom and anxiety. The breed's size and energy level make them suitable for urban living, but they should not be confined for long periods, as this can lead to behavioral issues.
Climate Preference
🍲Feeding Guide
Schedule
Food Types
Portion Size
Special Nutritional Needs
Miniature Schnauzers may be prone to health issues related to high-fat diets, such as hyperlipidemia and pancreatitis. It's essential to feed them low-fat, high-quality foods and avoid sugary treats. Regular veterinary check-ups can help monitor their weight and overall health, and adjustments to their diet may be necessary based on their activity level and age.
✨Grooming Requirements
Grooming Overview
Miniature Schnauzers have a wiry double coat that requires regular grooming to maintain its health and appearance. Owners should brush their Miniature Schnauzer at least once or twice a week to prevent matting and tangles.
Regular grooming appointments are recommended every 4 to 8 weeks, depending on whether the coat is clipped or stripped. Clipping is common for pet schnauzers, resulting in a softer coat, while stripping is preferred for show dogs to maintain the wiry texture.
Special attention should be given to the beard and eyebrows, as they can trap food and moisture, leading to skin issues if not cleaned regularly.
Care Schedule
Brush weekly, groom every 4-8 weeks (clipping or stripping).
Health Profile
⚕️Health Care
Regular veterinary care is crucial for the longevity of Miniature Schnauzers. Routine check-ups, vaccinations, and preventive treatments can help catch potential health issues early.
Dental care is also important, as dental disease can lead to other health complications. Owners should establish a healthcare routine that includes regular vet visits, vaccinations, and preventive care to support their dog's health throughout its life.
Health Issues Overview
⏳Average Lifespan
Genetic Factors
Genetics plays a significant role in the lifespan of Miniature Schnauzers. Responsible breeding practices can help reduce the risk of hereditary health issues.
Potential owners should seek reputable breeders who conduct health testing for common conditions in the breed. Genetic diversity is essential for maintaining a healthy population, and prospective owners should inquire about the lineage of their chosen puppy to ensure a healthy genetic background.
Living Conditions
Miniature Schnauzers thrive in environments that provide regular interaction with their owners and opportunities for exercise. Living in a home with a yard is ideal, but they can adapt well to apartment living if given sufficient daily walks and playtime.
Their lifespan can be positively influenced by a stable environment, regular exercise, and mental stimulation. Stressful situations or lack of social interaction can negatively impact their health and longevity.
🏥Common Health Issues
Hyperlipidemia
Warning Signs
🔬Diagnosis
Blood tests to measure lipid levels.
💊Treatment
Dietary changes, medication if necessary.
📝Management Tips
Feed low-fat diets, monitor weight, and consult a veterinarian for dietary recommendations.
Diabetes
Warning Signs
🔬Diagnosis
Blood tests to measure glucose levels.
💊Treatment
Insulin therapy, dietary management.
📝Management Tips
Maintain a healthy weight, regular exercise, and a balanced diet.
Von Willebrand Disease (vWD)
Warning Signs
🔬Diagnosis
Blood tests to assess clotting ability.
💊Treatment
No cure; management focuses on preventing bleeding.
📝Management Tips
Avoid situations that could lead to bleeding; consult a veterinarian for management strategies.
🛡️Preventive Care
🔬Von Willebrand Disease Test
Tests for von Willebrand Disease assess the dog's ability to form blood clots, which is crucial for preventing excessive bleeding.
📅 Every 1-2 years, or as recommended by a veterinarian.
🔬Ophthalmic Examination
Eye examinations can help detect hereditary eye conditions common in Miniature Schnauzers, ensuring early intervention if necessary.
📅 Annually, or as recommended by a veterinarian.
🔬Cardiac Evaluation
Cardiac evaluations can help identify heart defects or conditions that may affect the breed.
📅 Every 1-2 years, especially in older dogs.
Training
🧠Intelligence & Trainability
💪Work Drive
Miniature Schnauzers thrive on mental stimulation and enjoy tasks that challenge their intelligence. Activities such as agility training, obedience trials, and interactive games can keep them mentally engaged.
Their history as working dogs means they appreciate having a 'job' to do, whether it's participating in dog sports or simply following their owners around the house. Without sufficient mental engagement, they may resort to undesirable behaviors, so it's essential to provide regular challenges to keep their minds sharp.
⚠️Training Considerations
Miniature Schnauzers can exhibit stubbornness, which may pose challenges during training. They may also have a high prey drive, leading them to chase smaller animals if not properly socialized.
To overcome these challenges, consistent training methods using positive reinforcement are recommended. Early socialization with various people, pets, and environments can help mitigate any aggressive tendencies towards strangers or other animals.
Providing mental stimulation through puzzle toys and interactive games can also prevent boredom-related behaviors.
📝Training Tips
Training a Miniature Schnauzer can be enjoyable due to their intelligence and eagerness to please. Start with basic obedience commands and gradually introduce more complex tasks.
Use positive reinforcement techniques, such as treats and praise, to encourage desired behaviors. Consistency is key; establish a routine and be patient, as they may take time to learn new commands.
Incorporating fun activities, like agility training or interactive games, can keep them engaged and motivated. Regular training sessions will help strengthen the bond between the dog and owner while ensuring good behavior.
History & Heritage
📜Origin Story
The Miniature Schnauzer's journey began in the late 1800s in southern Germany, where farmers aimed to create a small yet robust dog capable of controlling vermin on farms. By crossing the Standard Schnauzer with smaller breeds like the Affenpinscher and Poodle, they produced a compact dog that retained the Schnauzer's intelligence and tenacity.
The breed was first exhibited in 1899, quickly gaining recognition for its unique characteristics. The Miniature Schnauzer's popularity soared in the post-World War II era, making it a favorite among families and dog lovers alike.
Today, it stands as a testament to the successful blending of utility and companionship in dog breeding.
⏳Development History
The Miniature Schnauzer was developed in Germany in the late 19th century, primarily from the Standard Schnauzer, Affenpinscher, and possibly the Poodle. Farmers sought a smaller dog that could effectively control vermin while being suitable for urban living.
The first recorded Miniature Schnauzer appeared in 1888, and by 1899, the breed was recognized as distinct from its larger counterparts. The American Kennel Club (AKC) accepted the breed for registration in 1926, and it has since gained immense popularity, particularly in the United States, where it is celebrated for its friendly demeanor and intelligence.
🛡️Purpose & Historical Role
Originally bred as a farm dog for ratting, the Miniature Schnauzer has evolved into a beloved companion and watchdog. Its keen senses and alert nature make it an excellent guardian, while its playful and affectionate demeanor endears it to families. The breed's versatility allows it to participate in various activities, including agility, obedience, and earthdog trials, showcasing its intelligence and adaptability.
🏺Cultural Significance
The Miniature Schnauzer has become a beloved companion dog worldwide, known for its charming personality and distinctive appearance. Its origins as a farm dog in Germany highlight its historical role in pest control, while its modern popularity reflects its adaptability to family life.
The breed's presence in popular culture, including literature and media, has further solidified its status as a cherished pet. Its ability to compete in various dog sports showcases its intelligence and versatility, making it a favorite among dog enthusiasts.
Conservation Status
The breed exists today and isn’t classified as extinct.
Often found in multiple regions; easier to encounter.
This breed is well-established with healthy population numbers.
?Frequently Asked Questions
Is the Miniature Schnauzer good for apartment living?
Yes, the Miniature Schnauzer generally does well in apartments. They adapt comfortably to smaller spaces and can thrive with regular walks and indoor play. Their temperament and energy level make them a good fit for apartment living, though they still need daily exercise.
How much does a Miniature Schnauzer shed?
The Miniature Schnauzer is a very low-shedding breed, making them an excellent choice for people who prefer minimal pet hair around the home. Regular grooming is still recommended to keep their coat healthy, but you won't find much fur on your furniture.
Are Miniature Schnauzers easy to train?
The Miniature Schnauzer can be moderate when it comes to training. They can learn commands and routines with consistent effort, though they may sometimes show a stubborn streak. Patience, positive reinforcement, and regular practice sessions will yield the best results.
How long do Miniature Schnauzers live?
The average lifespan of a Miniature Schnauzer is 12 - 14 years. Lifespan can be influenced by genetics, diet, exercise, and overall health care. Regular veterinary check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can help your Miniature Schnauzer live a long and happy life.
Is the Miniature Schnauzer good with kids?
Yes, the Miniature Schnauzer generally does well with children. They are patient and affectionate, making them a solid family dog. As with any breed, supervision during interactions with young children is always recommended.
How much exercise does a Miniature Schnauzer need?
The Miniature Schnauzer requires approximately 30 minutes of daily exercise. A combination of walks, play sessions, and mental stimulation activities will help keep them fit and happy. This is a moderate exercise requirement that fits well into most active lifestyles.
Is the Miniature Schnauzer good with other pets?
The Miniature Schnauzer can be moderate around other pets. They can get along with other animals when properly introduced and socialized from an early age. Gradual introductions and positive associations will help build harmonious relationships.